
The boot code that is loaded during a system’s initial configuration, such as the firmware and OS version components, may be examined and saved in the TPM. The most widely employed TPM functions include key generation and usage, as well as measures of system security.
The TCG cautions that due to its vulnerability to manipulation and any potential operating system security flaws, real-time usage of this is not encouraged. The virtual TPM, an integral part of the cloud-based architecture, gives every virtual machine a unique set of commands, much like a conventional TPM would. A virtual TPM is a creative technique to deploy a TPM in a cloud setting. TPMs can be physically included in the primary CPU or operate as software in an exclusive environment called firmware.
There are basically four kinds of TPMs, according to the Trusted Computing Group (TCG), which regulates TPM guidelines. TPM-based keys can also be configured to demand an authorization value. Since the key cannot be duplicated and used without the TPM, this helps to lessen phishing attempts. One option is to avoid a TPM-based key being used outside the TPM. There are several configuration options for TPM-based keys. TPMs, on the other hand, are hardware chips with various security safeguards that prevent tampering and malicious software from interfering with their security features. However, the software is “elastic”, its code can always be tampered with, allowing trespassers to access private data. When appropriately executed, software security is an effective instrument for preventing hackers from accessing a network.
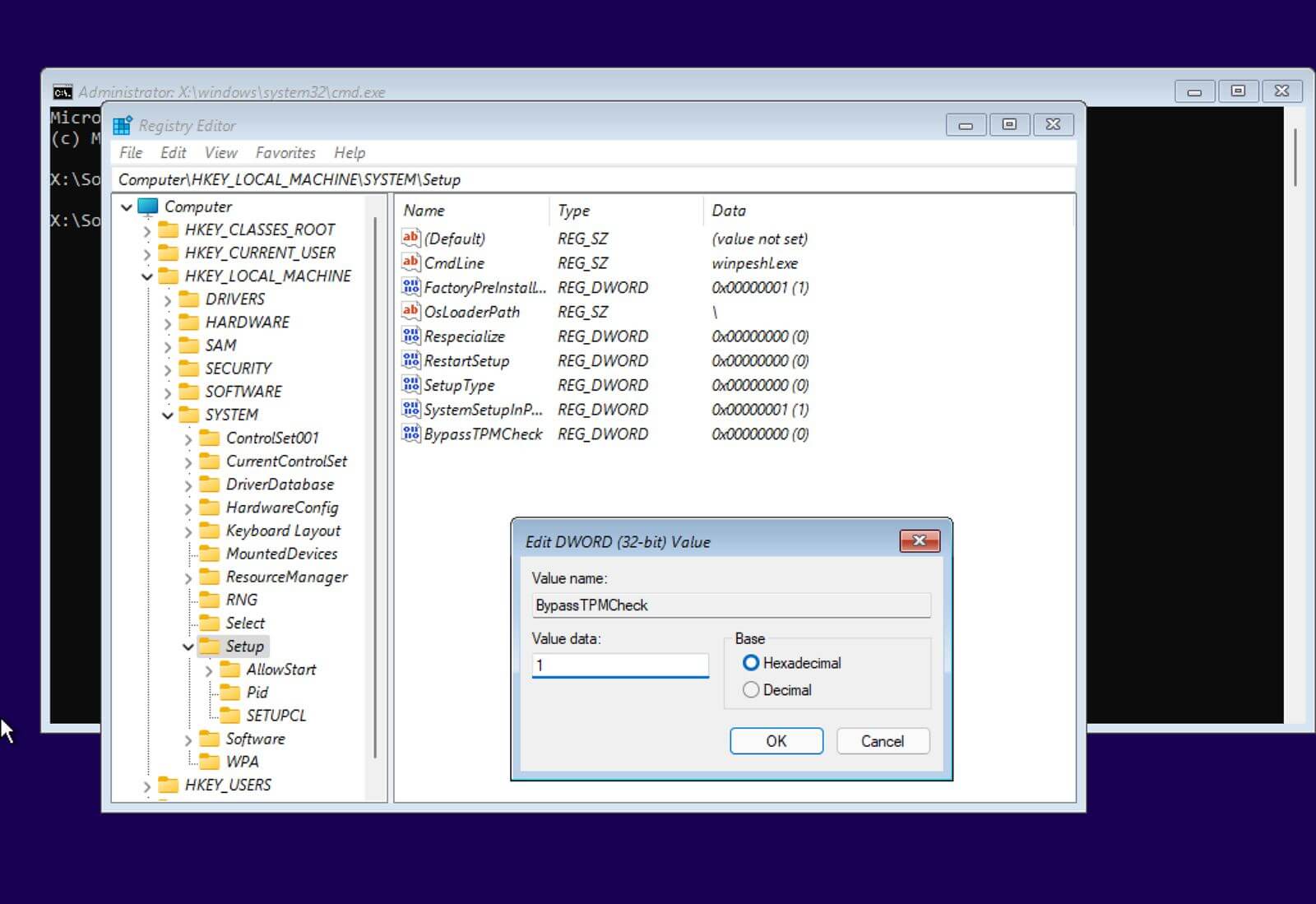
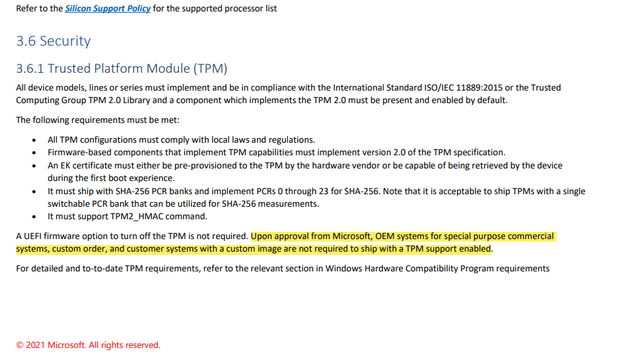
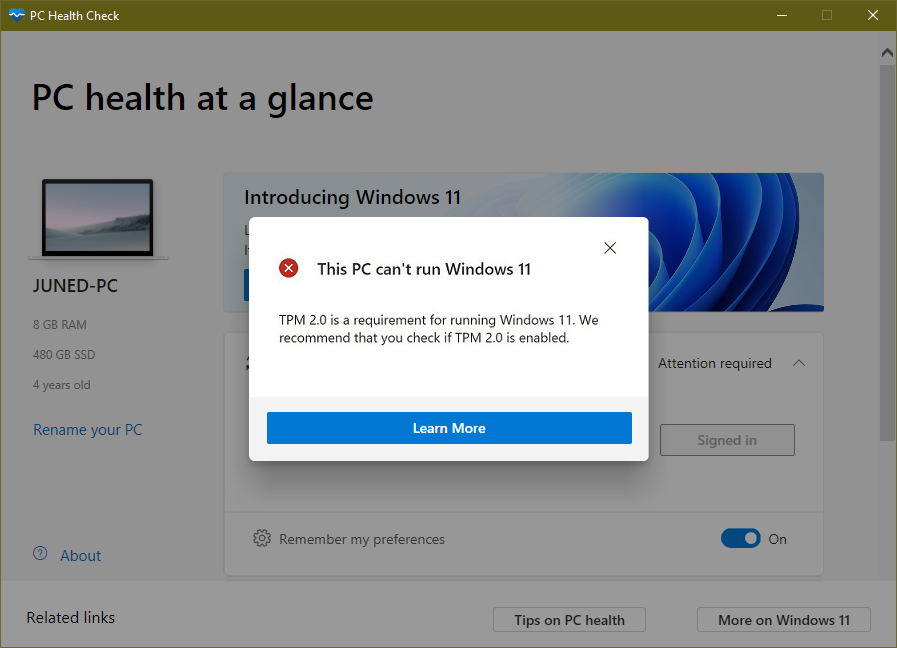
So, network administrators are now checking their devices to see if they were manufactured with a TPM and whether they are sufficient for an OS upgrade. Microsoft has officially announced that enabling TPM 2.0 is mandatory for installation or migration to Windows 11. TPM is the new talk of the town, especially after Microsoft announced the hardware requirements of the recently released Windows 11. It is usually located on your system’s hardware (primarily the motherboard), occasionally independent from the memory and the primary CPU. A TPM (Trusted Platform Module) is a cryptoprocessor that enhances the security of any hardware-based system by generating and securely storing cryptographic keys.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
